Linux-关于 fdisk 命令
1. fdisk 命令是什么
[!citation] > https://wangchujiang.com/linux-command/c/fdisk.html
- 用来完成磁盘分区的管理工作
- 比如创建、删除、修改分区的大小和对应的文件系统
- 常见操作如下
sh
fdisk [选项] <磁盘> 更改分区表
fdisk [选项] -l [<磁盘>...] 列出分区表
选项:
-b, --sectors-size <大小> 显示扇区计数和大小
-B, --protect-boot 创建新标签时不要擦除 bootbits
-c, --compatibility[=<模式>] 模式,为“dos”或“nondos”(默认)
-L, --color[=<时机>] 彩色输出(auto, always 或 never)默认启用颜色
-l, --list 显示分区并退出
-x, --list-details 类似 --list 但提供更多细节
-n, --noauto-pt 不要在空设备上创建默认分区表
-o, --output <列表> 输出列
-t, --type <类型> 只识别指定的分区表类型
-u, --units[=<单位>] 显示单位,“cylinders”柱面或“sectors”扇区(默认)
-s, --getsz 以 512-字节扇区显示设备大小[已废弃]
-b, --bytes 以字节为单位而非易读的格式来打印 SIZE
--lock[=<模式>] 使用独占设备锁(yes、no 或 nonblock)
-w, --wipe <模式> 擦除签名(auto, always 或 never)
-W, --wipe-partitions <模式> 擦除新分区的签名(auto, always 或 never)
-C, --cylinders <数字> 指定柱面数
-H, --heads <数字> 指定磁头数
-S, --sectors <数字> 指定每条磁道的扇区数
-h, --help 显示此帮助
-V, --version 显示版本2. 常见的 fdisk 命令的操作
2.1 如何删除现有的分区?
在实验环境下,首先查看
/dev/sdc, 然后删除该磁盘下所有的物理分区。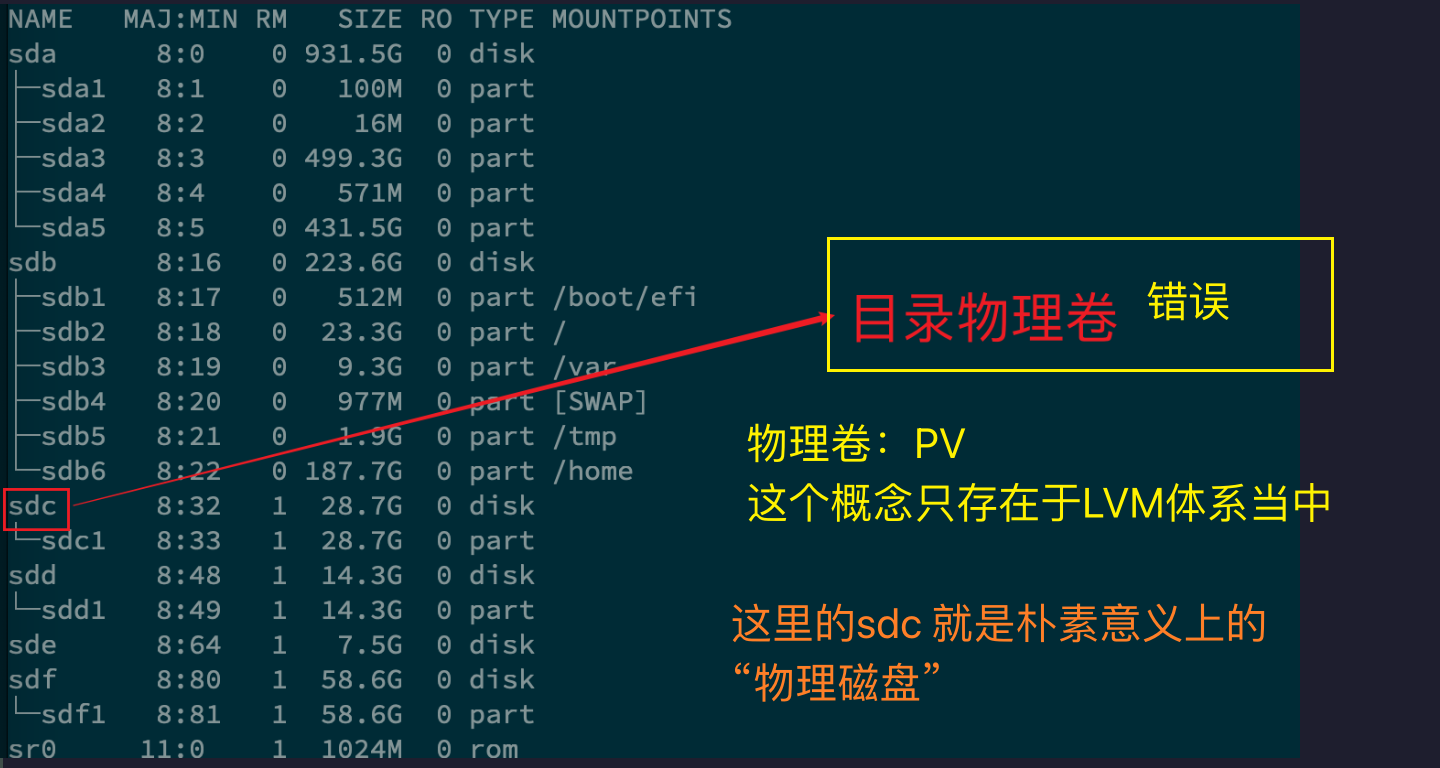
sudo fdisk /dev/sdc进入交互式页面进行查看交互式页面下输入:
m查看可选命令
交互式命令下输入
p,查看目标物理卷 (PV) 上所有的分区情况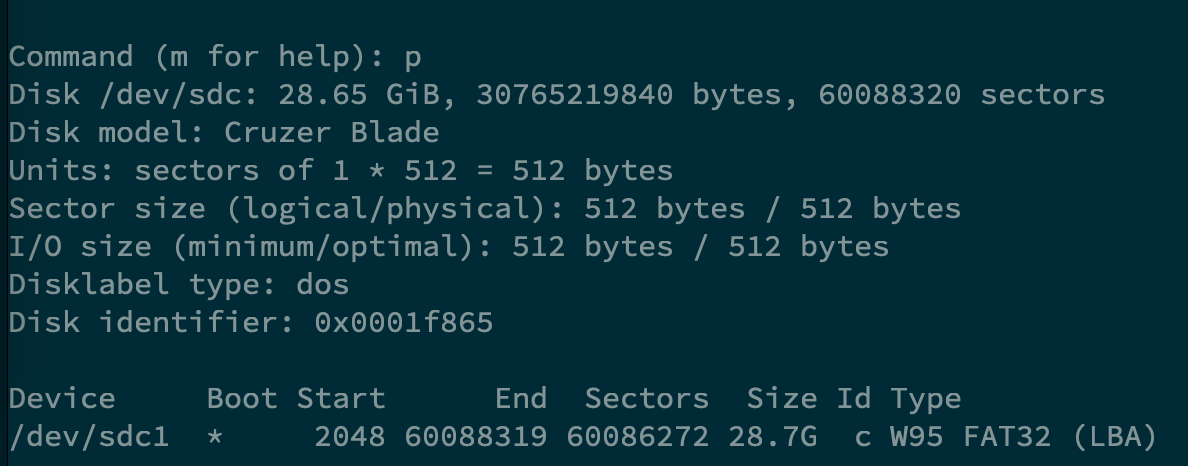
可以看出,文件系统是
FAT32,以及分区的一些情况
- 删除特定分区之前,首先需要确保分区已经被
umount了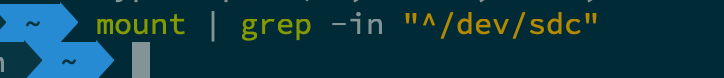
- 删除特定分区,
d {n},n 就是分区号,比如这里希望删除/dev/sdc1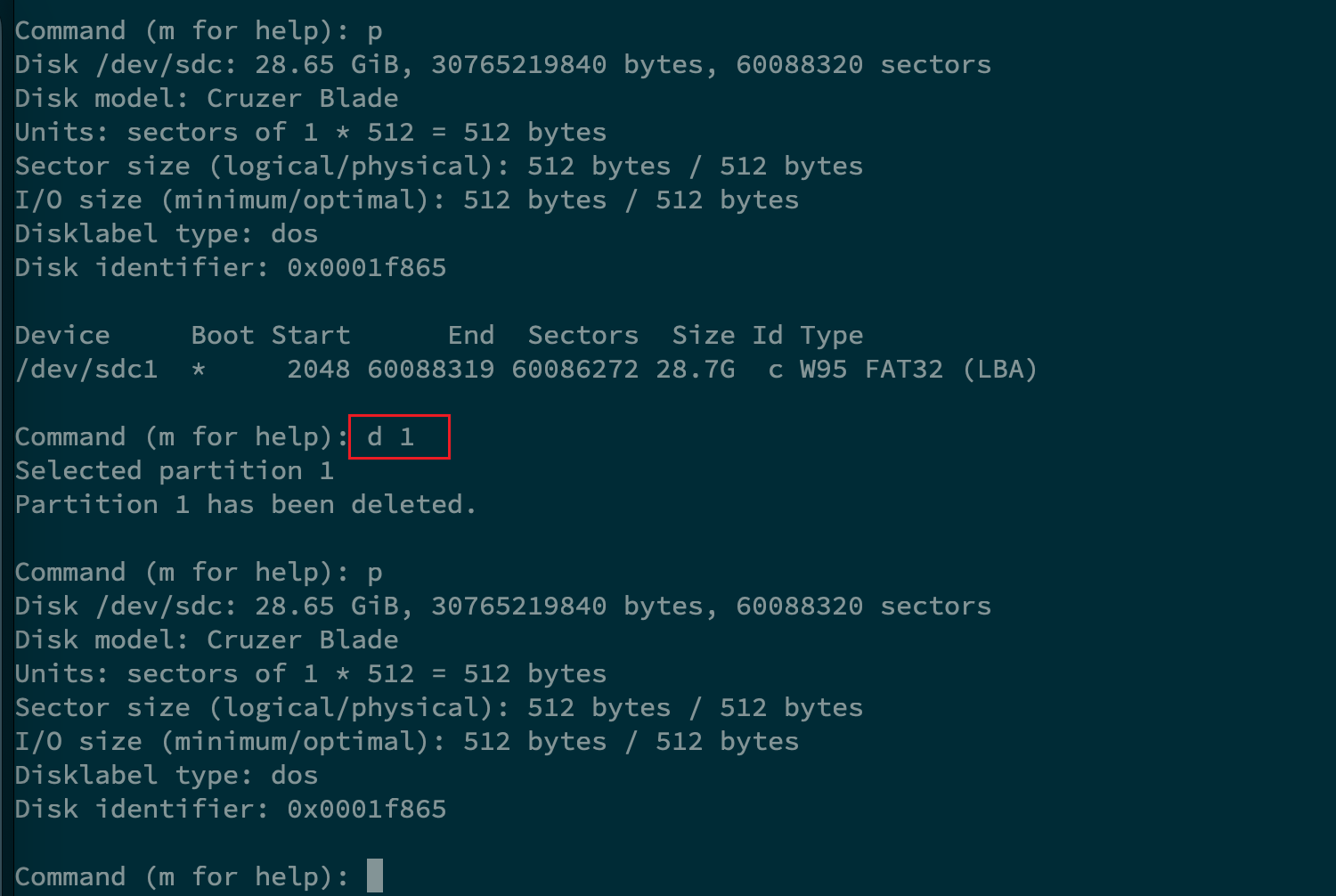
- 需要输入
w来保存写入之后的修改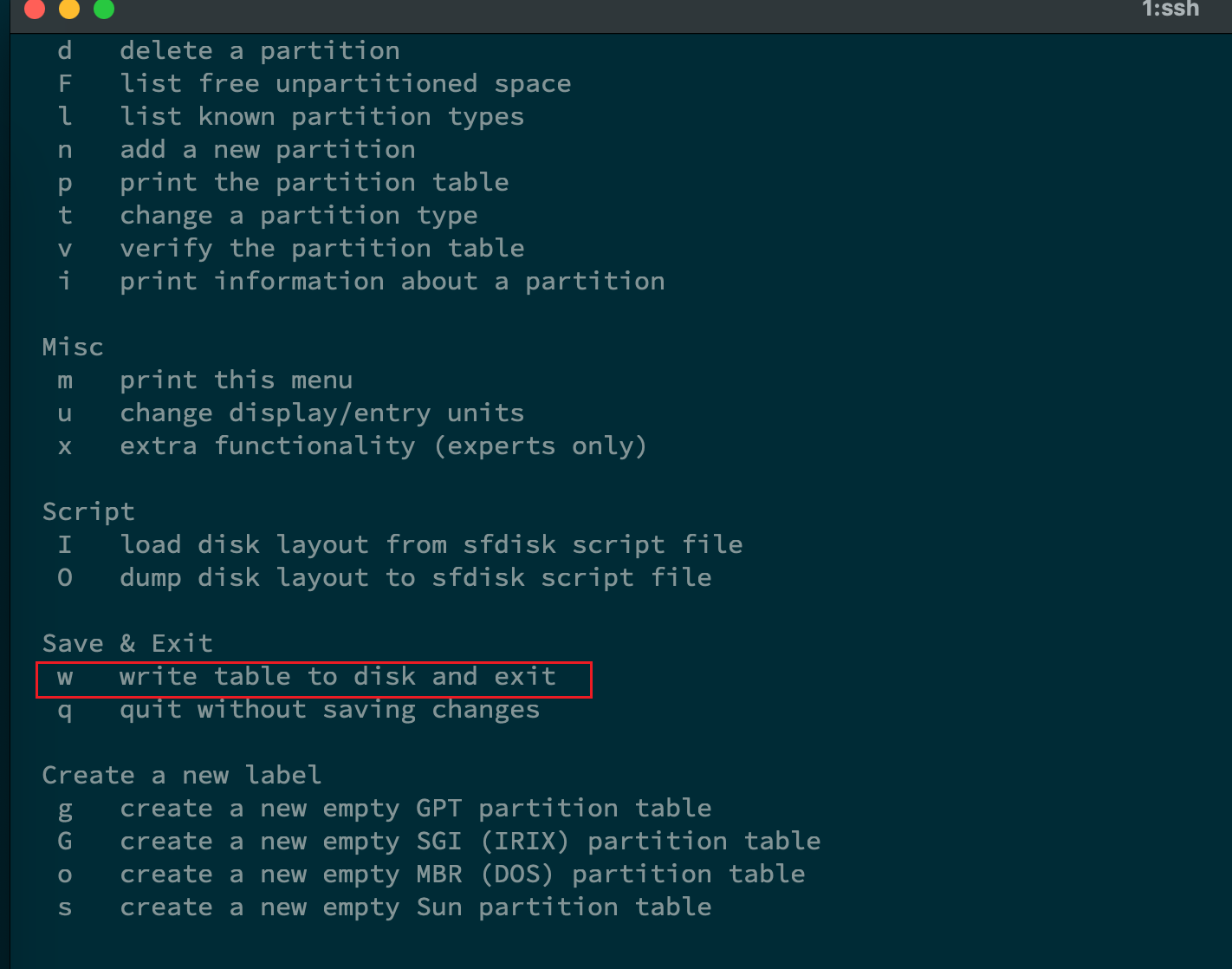
- 该分区已经成功删除了
2.2 建立两个新分区
首先,在交互页面下输入
F,用来查看还有多少空间尚未被分区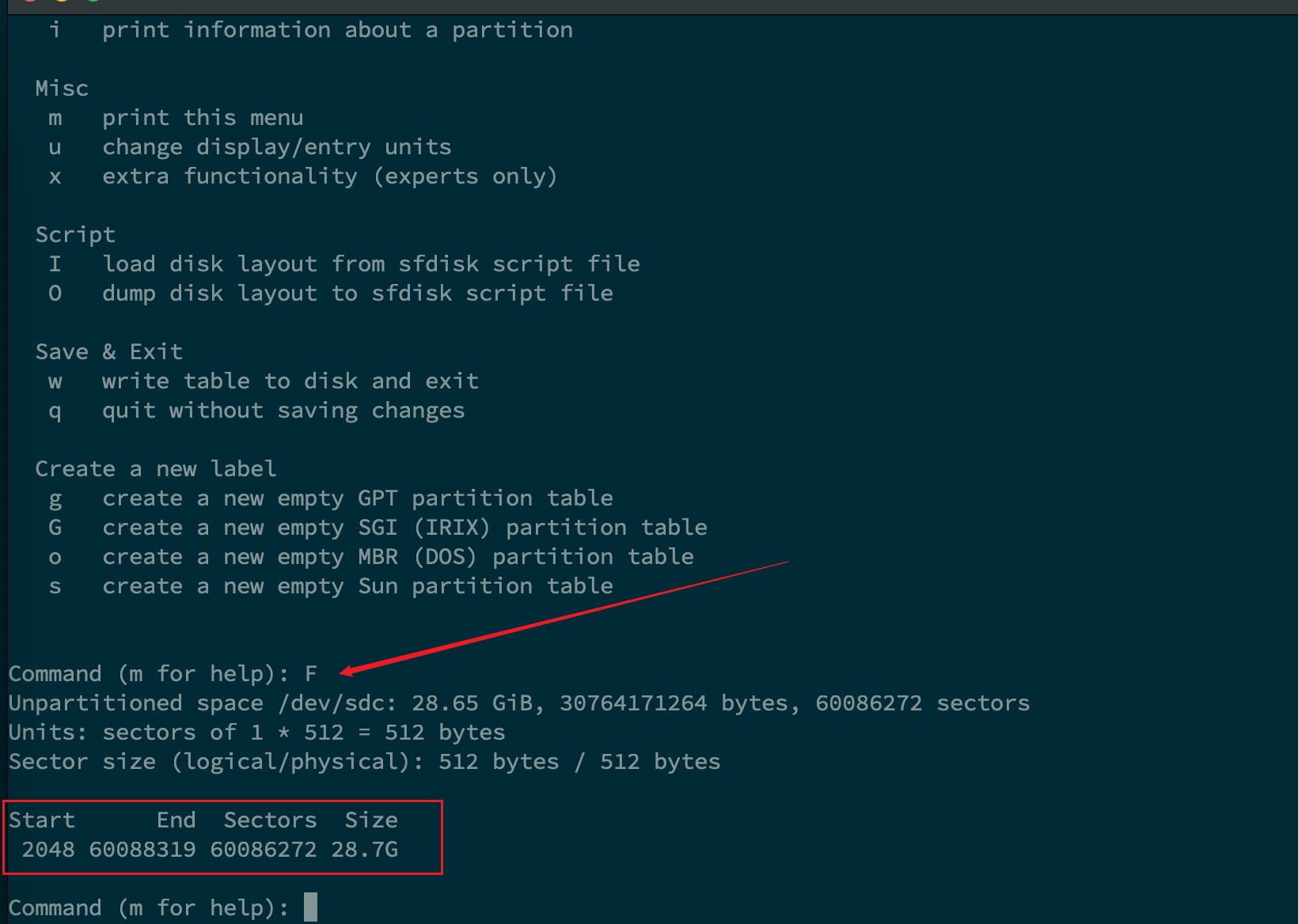
划分三个分区,其大小为
1/2/1.5 GB,以第 2 个分区为例
sh
# fdisk /dev/sdc
Command (m for help): n # 创建新分区
Partition type
p primary (1 primary, 0 extended, 3 free)
e extended (container for logical partitions)
Select (default p): p # 指定分区类型为Primary
Partition number (2-4, default 2):
First sector (2099200-60088319, default 2099200): # 指定第一个扇区的位置
Last sector, +/-sectors or +/-size{K,M,G,T,P} (2099200-60088319, default 60088319): +2G # 利用+号指定偏移量大小为2G
Created a new partition 2 of type 'Linux' and of size 2 GiB.这里的分区的
Primary和extended有什么区别?分区是直接位于分区表中的分区,用于存储数据和安装操作系统,而扩展分区是一种特殊的主分区,用作逻辑分区的容器。
全部划分完毕之后,应该如下所示:
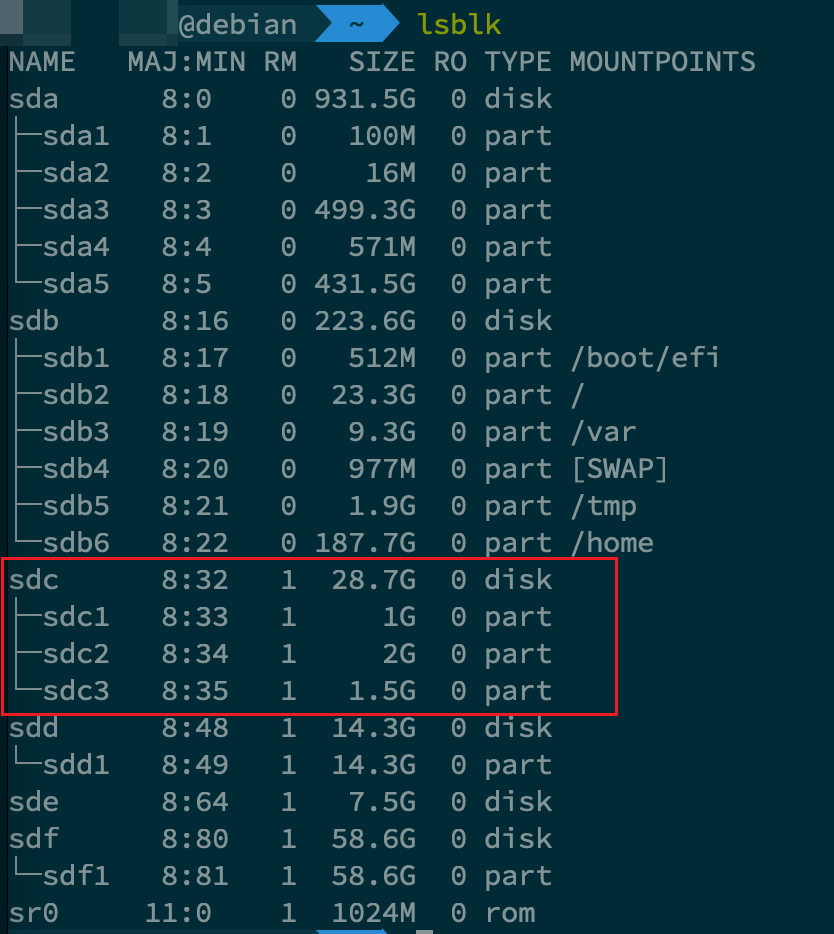
2.3 扩展某个分区
- 将
/dev/sdc2分区空间设置为5G - 操作就是先删,再建
- 删除操作如下
sh
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdc: 28.65 GiB, 30765219840 bytes, 60088320 sectors
Disk model: Cruzer Blade
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disklabel type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x0001f865
Device Boot Start End Sectors Size Id Type
/dev/sdc1 2048 2099199 2097152 1G 83 Linux
/dev/sdc2 2099200 6293503 4194304 2G 83 Linux
/dev/sdc3 6293504 9439231 3145728 1.5G 83 Linux
Command (m for help): d 2
Partition number (1-3, default 3): 2
Partition 2 has been deleted.
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdc: 28.65 GiB, 30765219840 bytes, 60088320 sectors
Disk model: Cruzer Blade
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disklabel type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x0001f865
Device Boot Start End Sectors Size Id Type
/dev/sdc1 2048 2099199 2097152 1G 83 Linux
/dev/sdc3 6293504 9439231 3145728 1.5G 83 Linux- 重新建立
/dev/sdc2,此时,如果选择原来的 扇区起始位置,那么就会出错,因为空间必须是连续的,试图在2G空余空间上建立5G的磁盘分区,显然是不成立的。具体表现如下:
sh
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdc: 28.65 GiB, 30765219840 bytes, 60088320 sectors
Disk model: Cruzer Blade
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disklabel type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x0001f865
Device Boot Start End Sectors Size Id Type
/dev/sdc1 2048 2099199 2097152 1G 83 Linux
/dev/sdc3 6293504 9439231 3145728 1.5G 83 Linux
Command (m for help): n
Partition type
p primary (2 primary, 0 extended, 2 free)
e extended (container for logical partitions)
Select (default p): p
Partition number (2,4, default 2):
First sector (2099200-60088319, default 2099200):
Last sector, +/-sectors or +/-size{K,M,G,T,P} (2099200-6293503, default 6293503): +5G
Value out of range. # error- 因此,想要使得新建空间的大小大于
5GB,我们必须使得/dev/sdc2起始扇区的位置合理,存在大于5G的连续空间用来放置新建的磁盘分区。
sh
Command (m for help): n
Partition type
p primary (2 primary, 0 extended, 2 free)
e extended (container for logical partitions)
Select (default p): p
Partition number (2,4, default 2): 2
First sector (2099200-60088319, default 2099200): 9439232
Last sector, +/-sectors or +/-size{K,M,G,T,P} (9439232-60088319, default 60088319): +5G
Created a new partition 2 of type 'Linux' and of size 5 GiB.
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdc: 28.65 GiB, 30765219840 bytes, 60088320 sectors
Disk model: Cruzer Blade
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disklabel type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x0001f865
Device Boot Start End Sectors Size Id Type
/dev/sdc1 2048 2099199 2097152 1G 83 Linux
/dev/sdc2 9439232 19924991 10485760 5G 83 Linux
/dev/sdc3 6293504 9439231 3145728 1.5G 83 Linux
Partition table entries are not in disk order.- 调整完毕后如上所示,注意,这里的
Type Linux指的是磁盘分区的Type,并非文件系统(比如ext4之类的)。此处的Linux Type,指明了该磁盘分区是用来放置普通的 Linux 文件的。
2.4 格式化和 fdisk 之间的关系
- 首先明确一个概念,格式化分区指的是擦除数据并且重新指定文件系统等一些列操作,具体解释如下
[!ai]
- 在格式化过程中,存储介质上的现有数据将被擦除,并根据所选择的文件系统类型重新创建文件系统结构和相关的元数据。这使得存储介质能够被操作系统识别,并能够存储和检索数据。
fdisk仅仅只是磁盘分区调整的相关操作,具体的格式化操作发生在这一步之后。
- 利用
lsblk -f查看块设备的情况,其中-f ==> file system, 利用这个参数可以实现打印文件系统的目的。 - 执行后,具体信息如下
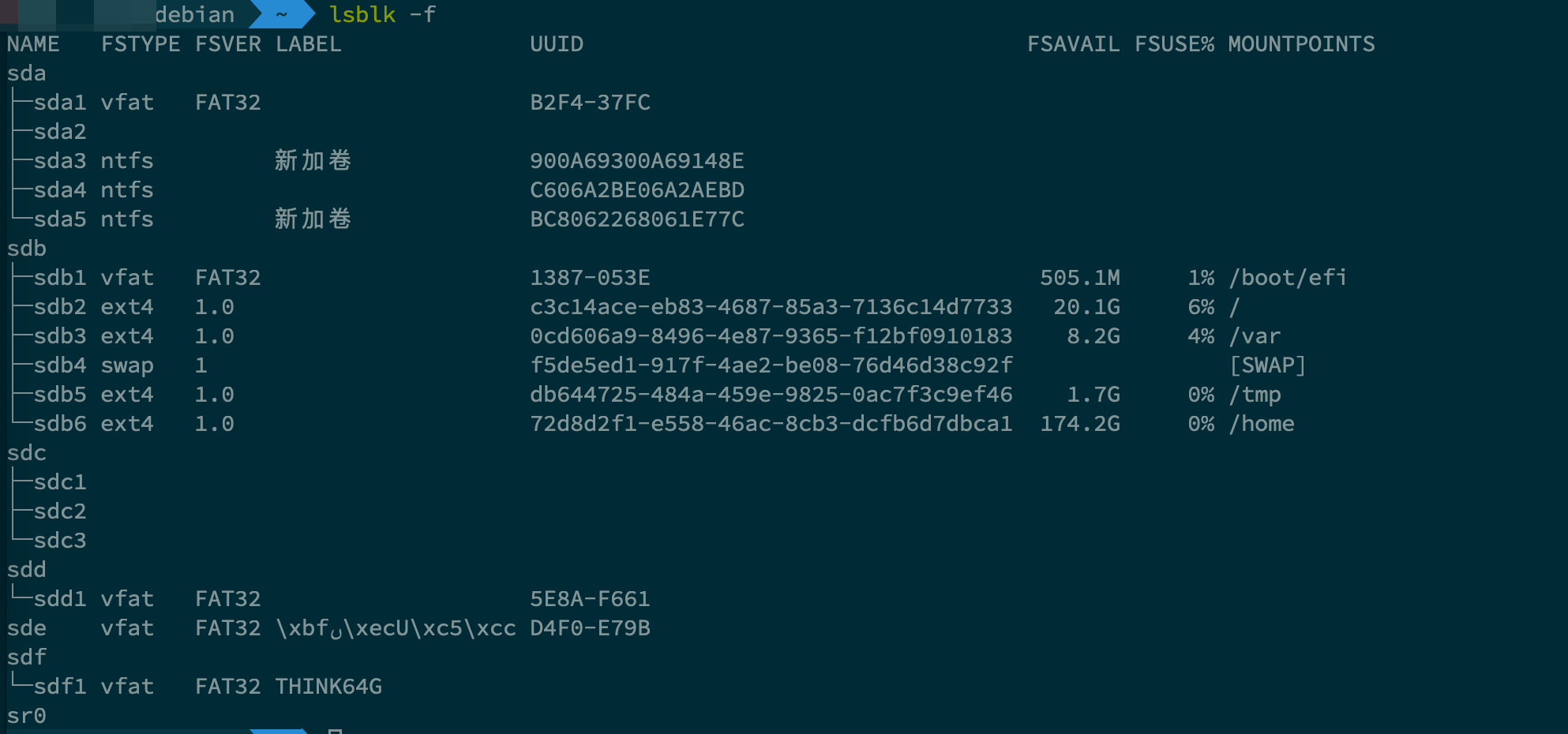
- 格式化的操作借助
mkfs.xxx来完成,比如最常见的ext4
sh
sudo mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdc3- 结果如下所示,可以看到,如果仅仅只是用
fdisk指定了磁盘分区,其文件系统是空的
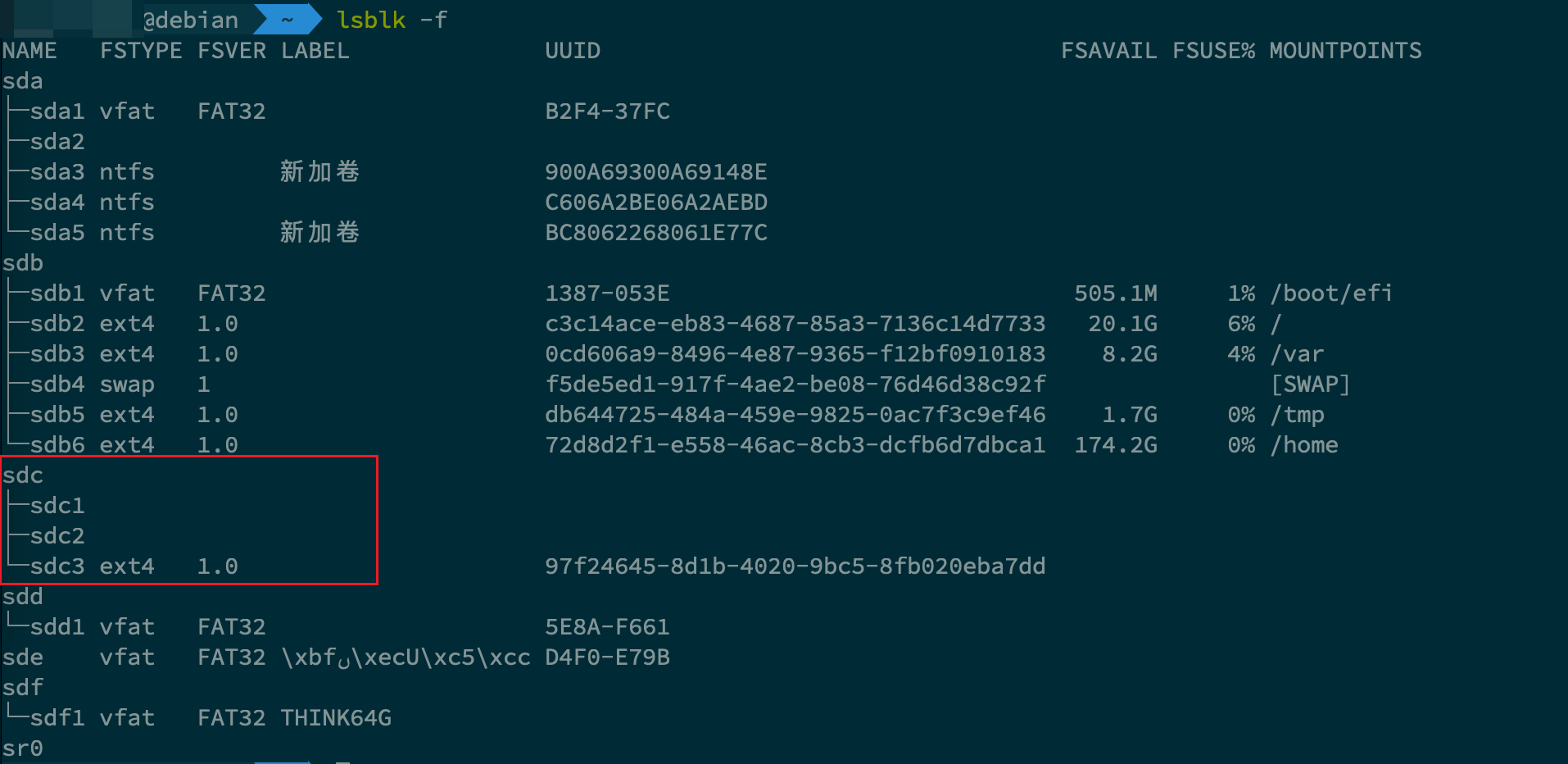
3. fdisk 和 LVM 之间的关系
fdisk操作当中,默认指定的磁盘分区类型是Linux,这个分区可以用来放置普通的文件数据。但是事实上,如果我们希望实现多个物理卷拼接为一个逻辑卷的场景,即实现LVM的需求,我们需要显式改变其磁盘分区的类型。- 以上面创建的 3 个逻辑分区为例,调整其
Type为LVM(对应状态码为8e - 在
fdisk交互页面当中,输入t即可修改分区类型,LVM对应hex code为8e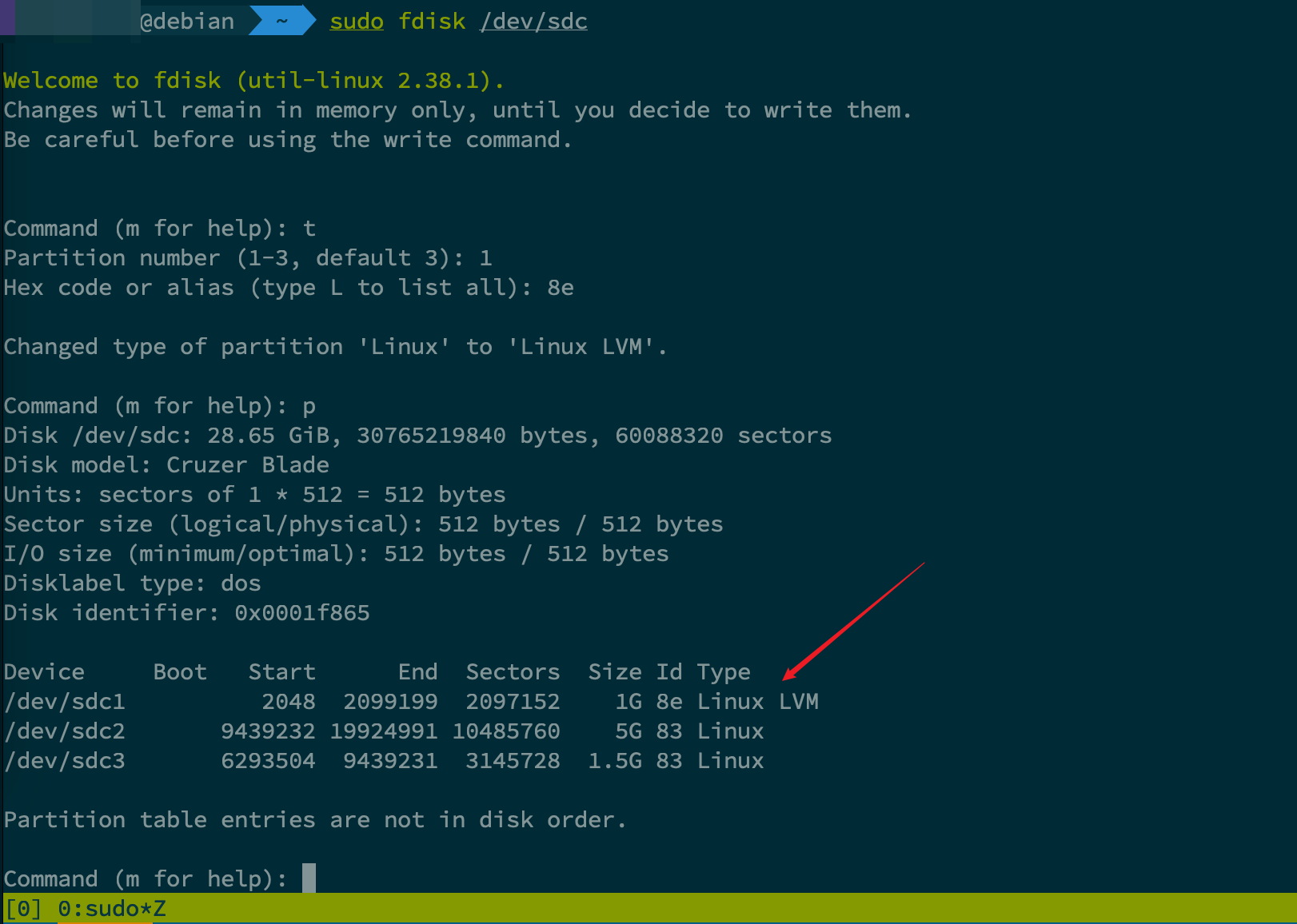
`